Key Insights
The China Waste to Energy (WTE) market is set for substantial growth, driven by increasing waste generation and the nation's commitment to sustainable energy and environmental protection. The market is projected to reach approximately USD 7.01 billion by 2024, expanding at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.94%. Key growth drivers include supportive government policies, rapid urbanization, and the imperative to reduce landfill dependency and greenhouse gas emissions. Technological advancements in WTE are enhancing facility efficiency and environmental responsibility, positioning China as a global leader in the sector.
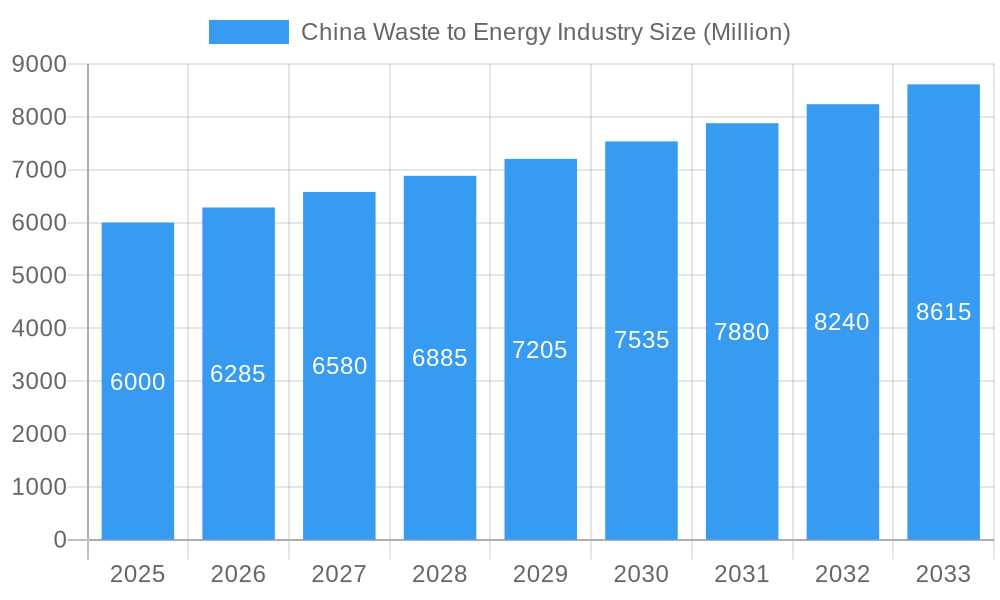
China Waste to Energy Industry Market Size (In Billion)
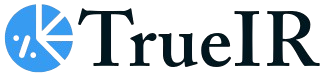
The WTE industry in China encompasses physical, thermal, and biological processes. Thermal WTE, primarily incineration with energy recovery, leads the market for municipal solid waste. However, anaerobic digestion and gasification are emerging as sustainable alternatives. Leading companies like Covanta Holding Corporation, Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc., Veolia Environnement SA, Zheneng Jinjiang Environment Holding Co Ltd, and China Everbright International Limited are actively expanding their presence. Challenges include high initial investment costs, public perception regarding emissions, and the need for standardized regulatory frameworks.
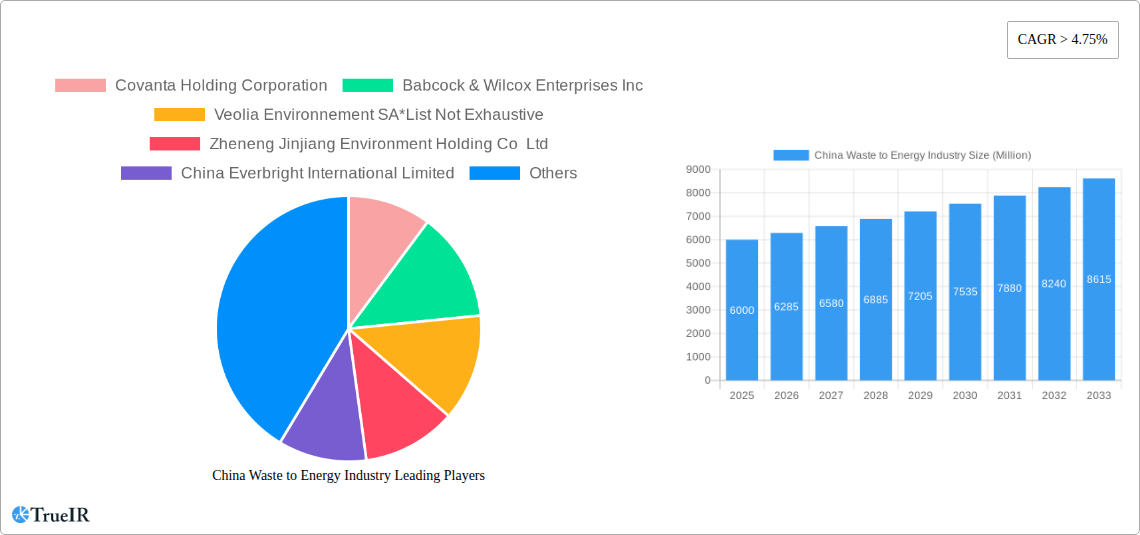
China Waste to Energy Industry Company Market Share
This report offers a detailed analysis of the China Waste to Energy Market, covering 2019-2033, with a base year of 2024. It examines market dynamics, technological innovations, and competitive strategies. Utilizing keywords such as "China waste to energy," "MSW to energy," "waste management China," "renewable energy China," and "RDF production," the report provides valuable insights for industry stakeholders, investors, and policymakers.
China Waste to Energy Industry Market Structure & Competitive Landscape
The China Waste to Energy industry exhibits a moderately concentrated market structure, driven by substantial infrastructure investments and stringent environmental regulations. Key players are increasingly consolidating their market share through strategic mergers and acquisitions, aiming to achieve economies of scale and technological advancements. Innovation drivers include the development of advanced combustion technologies, enhanced flue gas treatment systems, and the optimization of refuse-derived fuel (RDF) production to maximize energy recovery and minimize emissions. Regulatory impacts are significant, with government policies promoting waste reduction, recycling, and the adoption of waste-to-energy (WtE) solutions playing a pivotal role. The industry faces competition from traditional waste disposal methods and, to a lesser extent, from alternative renewable energy sources. End-user segmentation is primarily driven by municipal waste generation and industrial waste streams. Recent M&A activities reflect a trend towards vertical integration and expansion into new geographical markets within China. For instance, the M&A volume is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars annually, indicating significant capital deployment. The concentration ratio for the top 5 players is estimated to be around 45%, showcasing a blend of dominant forces and a sizable number of smaller participants.
China Waste to Energy Industry Market Trends & Opportunities
The China Waste to Energy Industry is poised for remarkable growth, projected to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 8.5% during the forecast period of 2025–2033. This robust expansion is fueled by China's relentless urbanization, leading to escalating volumes of municipal solid waste (MSW) and a corresponding surge in demand for sustainable waste management solutions. The market size is estimated to grow from over $15 Billion in 2025 to over $30 Billion by 2033, reflecting substantial investment and capacity build-out. Technological shifts are a prominent trend, with a move towards more efficient and environmentally friendly incineration technologies, alongside advancements in anaerobic digestion and gasification processes for biological waste streams. The adoption of Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) production is gaining significant traction, enabling the conversion of low-calorific value waste into high-energy fuel, thereby enhancing the economic viability of waste-to-energy projects.
Consumer preferences, particularly at the municipal level, are increasingly shifting towards cleaner energy sources and more effective waste disposal methods, directly impacting the demand for WtE infrastructure. Competitive dynamics are intensifying as both domestic and international players vie for market dominance. Opportunities abound for companies that can offer integrated waste management solutions, including collection, processing, and energy generation, coupled with robust emissions control technologies. The penetration rate of waste-to-energy solutions in China, though growing, still has significant room for expansion compared to developed nations, presenting a vast untapped market potential. Emerging opportunities also lie in the development of smart waste management systems that leverage IoT and AI for optimized waste collection and processing. Furthermore, the government's continued emphasis on achieving carbon neutrality targets by 2060 will further accelerate investments in waste-to-energy as a key pillar of its renewable energy strategy. The drive for circular economy principles is also creating new avenues for innovation in waste valorization and resource recovery.
Dominant Markets & Segments in China Waste to Energy Industry
The dominant market within the China Waste to Energy Industry is unequivocally the Thermal segment, particularly incineration-based technologies. This dominance is driven by the sheer volume of municipal solid waste (MSW) generated across China's rapidly urbanizing landscape, coupled with the mature and proven nature of thermal treatment processes. Infrastructure development has been a key growth driver, with the Chinese government heavily investing in the construction of large-scale incineration plants to address the growing waste crisis. Policies promoting WtE as a solution for both waste management and energy generation have been instrumental in this segment's expansion. The market size for the Thermal segment is projected to reach over $25 Billion by 2033, accounting for approximately 85% of the total market value.
Within the Thermal segment, incineration of MSW represents the largest sub-segment, accounting for an estimated 70% of the thermal capacity. The remaining 30% is comprised of specialized thermal treatments like gasification and pyrolysis, which are gaining traction due to their potential for higher energy efficiency and the production of valuable by-products. The Physical segment, encompassing mechanical biological treatment (MBT) and other physical separation processes, plays a crucial role in pre-treatment and resource recovery but is generally considered a supporting segment to thermal processes. Its market size is estimated to be around $2 Billion by 2033. The Biological segment, which includes anaerobic digestion and composting, is growing but currently holds a smaller market share, estimated at approximately $3 Billion by 2033. This is due to the specific suitability of biological treatment for organic waste streams and the challenges associated with scaling these processes for large volumes of mixed MSW. However, with increasing focus on biogas production and the valorization of organic waste, the Biological segment is expected to witness a significant CAGR of over 10% in the coming years. The dominance of the Thermal segment is further solidified by its ability to handle diverse waste compositions and its established operational track record, making it the preferred choice for many municipal waste management authorities in China.
China Waste to Energy Industry Product Analysis
The China Waste to Energy industry is characterized by continuous product innovation focused on enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and maximizing energy recovery. Key product advancements include the development of advanced boiler designs for higher thermal efficiency and lower operational costs, as well as sophisticated flue gas treatment systems employing technologies like selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and activated carbon injection to meet stringent environmental standards. Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) production plants are also a significant product innovation, enabling the conversion of low-calorific value waste into a standardized, high-energy fuel source suitable for co-firing in industrial boilers or dedicated WtE facilities. Competitive advantages are derived from technological superiority, operational reliability, and adherence to evolving environmental regulations. The market fit for these products is strong, addressing China's urgent need for sustainable waste management and renewable energy solutions.
Key Drivers, Barriers & Challenges in China Waste to Energy Industry
Key Drivers:
- Escalating MSW Generation: Rapid urbanization and population growth are leading to a significant increase in municipal solid waste, creating an urgent need for effective disposal and resource recovery.
- Government Support and Policies: Favorable government policies, including subsidies, feed-in tariffs, and renewable energy targets, are a major catalyst for WtE project development.
- Environmental Concerns: Growing public awareness and stricter environmental regulations regarding landfill emissions and pollution are pushing for cleaner waste management solutions like WtE.
- Energy Security and Renewable Energy Goals: WtE contributes to China's renewable energy targets and reduces reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing energy security.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous improvements in WtE technologies are increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impact.
Barriers & Challenges:
- High Initial Capital Investment: WtE plants require substantial upfront capital, posing a challenge for project financing, especially for smaller municipalities.
- Regulatory Complexity and Permitting: Navigating complex environmental regulations and obtaining necessary permits can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Supply Chain for MSW: Ensuring a consistent and high-quality supply of MSW to WtE facilities can be difficult due to varying waste collection systems and potential competition from recycling efforts.
- Public Perception and NIMBYism: Concerns about air pollution and potential health impacts can lead to public opposition and "Not In My Backyard" (NIMBY) sentiments.
- Competition from Alternative Waste Management: Growing emphasis on recycling and waste reduction can divert waste streams away from WtE facilities, impacting operational capacity and revenue. The cost of tipping fees, estimated to range from $15 to $30 per ton, is a crucial factor influencing the economic viability of WtE projects.
Growth Drivers in the China Waste to Energy Industry Market
Several critical factors are propelling the growth of the China Waste to Energy Industry. Technologically, advancements in efficiency and emissions control are making WtE plants more attractive and environmentally compliant. Economically, the increasing cost of landfilling and the economic benefits of energy generation from waste are strong incentives. Regulatory drivers, such as government mandates for renewable energy adoption and stringent waste management policies, provide a stable and supportive framework for investment. The ongoing urbanization and industrialization in China directly translate to higher waste generation volumes, presenting a consistent feedstock for WtE facilities. Furthermore, the global push towards a circular economy emphasizes resource recovery and waste valorization, positioning WtE as a key component of sustainable development strategies.
Challenges Impacting China Waste to Energy Industry Growth
Despite its promising trajectory, the China Waste to Energy Industry faces significant hurdles. Regulatory complexities surrounding permitting, environmental impact assessments, and evolving emission standards can slow down project development and increase compliance costs. Supply chain issues, including the variability of waste composition and quantity, and competition for feedstock from the recycling sector, can impact the operational efficiency and economic viability of WtE plants. Competitive pressures arise not only from other WtE operators but also from alternative energy sources and increasingly efficient traditional waste disposal methods. The initial capital expenditure for constructing state-of-the-art WtE facilities is substantial, often exceeding $100 Million per plant, posing a considerable barrier to entry and expansion. Maintaining consistent operational performance and managing public perception also remain ongoing challenges.
Key Players Shaping the China Waste to Energy Industry Market
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc
- Veolia Environnement SA
- Zheneng Jinjiang Environment Holding Co Ltd
- China Everbright International Limited
Significant China Waste to Energy Industry Industry Milestones
- October 2022: Jieyang Green Fuel Plant successfully commissioned after a 21-day performance testing period. The Jieyang plant converts 401,500 t/a municipal solid waste (MSW) into refuse-derived fuel (RDF) with high calorific value and recyclables.
- No other recent developments in the market studied.
Future Outlook for China Waste to Energy Industry Market
The future outlook for the China Waste to Energy Industry is exceptionally bright, driven by a confluence of robust market trends and strategic opportunities. As China continues its aggressive pursuit of carbon neutrality and sustainable development goals, the demand for efficient and environmentally sound waste management solutions will only intensify. Investments in advanced WtE technologies, including improved waste-to-power efficiency and enhanced emission control systems, are expected to accelerate. The expansion of RDF production and the integration of biological treatment methods for organic waste present significant growth catalysts. Furthermore, a growing emphasis on circular economy principles will foster innovation in waste valorization, creating new revenue streams and enhancing the overall sustainability of the sector. The market is projected to witness substantial growth, with significant opportunities for both domestic and international players willing to invest in cutting-edge technologies and sustainable operational practices.
China Waste to Energy Industry Segmentation
- 1. Physical
- 2. Thermal
- 3. Biological
China Waste to Energy Industry Segmentation By Geography
- 1. China
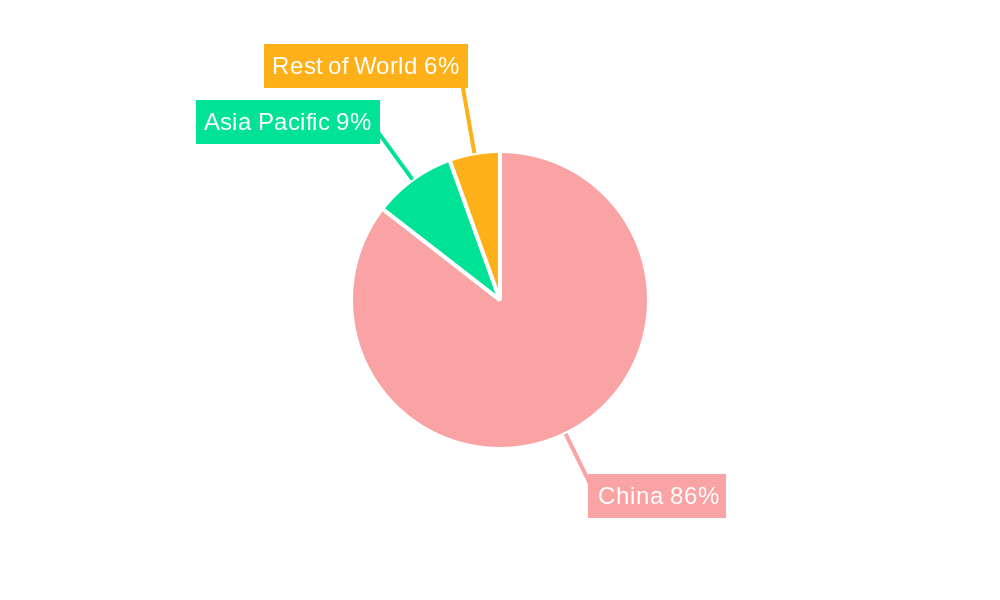
China Waste to Energy Industry Regional Market Share
Geographic Coverage of China Waste to Energy Industry
China Waste to Energy Industry REPORT HIGHLIGHTS
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2020-2034 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Estimated Year | 2026 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 8.94% from 2020-2034 |
| Segmentation |
|
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 1.1. Research Scope
- 1.2. Market Segmentation
- 1.3. Research Methodology
- 1.4. Definitions and Assumptions
- 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Introduction
- 3. Market Dynamics
- 3.1. Introduction
- 3.2. Market Drivers
- 3.2.1. 4.; Increasing Electricity Demand4.; Rsing Investments in the Coal Industry
- 3.3. Market Restrains
- 3.3.1. 4.; Increasing Installation of Renewable Energy Sources
- 3.4. Market Trends
- 3.4.1. Thermal-based Waste-to-Energy Conversion to Dominate the Market
- 4. Market Factor Analysis
- 4.1. Porters Five Forces
- 4.2. Supply/Value Chain
- 4.3. PESTEL analysis
- 4.4. Market Entropy
- 4.5. Patent/Trademark Analysis
- 5. China Waste to Energy Industry Analysis, Insights and Forecast, 2020-2032
- 5.1. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Physical
- 5.2. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Thermal
- 5.3. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Biological
- 5.4. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Region
- 5.4.1. China
- 5.1. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Physical
- 6. Competitive Analysis
- 6.1. Market Share Analysis 2025
- 6.2. Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Covanta Holding Corporation
- 6.2.1.1. Overview
- 6.2.1.2. Products
- 6.2.1.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.1.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.1.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.2 Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc
- 6.2.2.1. Overview
- 6.2.2.2. Products
- 6.2.2.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.2.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.2.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.3 Veolia Environnement SA*List Not Exhaustive
- 6.2.3.1. Overview
- 6.2.3.2. Products
- 6.2.3.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.3.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.3.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.4 Zheneng Jinjiang Environment Holding Co Ltd
- 6.2.4.1. Overview
- 6.2.4.2. Products
- 6.2.4.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.4.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.4.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.5 China Everbright International Limited
- 6.2.5.1. Overview
- 6.2.5.2. Products
- 6.2.5.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.5.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.5.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.1 Covanta Holding Corporation
List of Figures
- Figure 1: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue Breakdown (billion, %) by Product 2025 & 2033
- Figure 2: China Waste to Energy Industry Share (%) by Company 2025
List of Tables
- Table 1: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Physical 2020 & 2033
- Table 2: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Thermal 2020 & 2033
- Table 3: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Biological 2020 & 2033
- Table 4: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Region 2020 & 2033
- Table 5: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Physical 2020 & 2033
- Table 6: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Thermal 2020 & 2033
- Table 7: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Biological 2020 & 2033
- Table 8: China Waste to Energy Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Country 2020 & 2033
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of the China Waste to Energy Industry?
The projected CAGR is approximately 8.94%.
2. Which companies are prominent players in the China Waste to Energy Industry?
Key companies in the market include Covanta Holding Corporation, Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc, Veolia Environnement SA*List Not Exhaustive, Zheneng Jinjiang Environment Holding Co Ltd, China Everbright International Limited.
3. What are the main segments of the China Waste to Energy Industry?
The market segments include Physical, Thermal, Biological.
4. Can you provide details about the market size?
The market size is estimated to be USD 7.01 billion as of 2022.
5. What are some drivers contributing to market growth?
4.; Increasing Electricity Demand4.; Rsing Investments in the Coal Industry.
6. What are the notable trends driving market growth?
Thermal-based Waste-to-Energy Conversion to Dominate the Market.
7. Are there any restraints impacting market growth?
4.; Increasing Installation of Renewable Energy Sources.
8. Can you provide examples of recent developments in the market?
In October 2022, Jieyang Green Fuel Plant was successfully commissioned after a 21-day performance testing period. The Jieyang plant converts 401.500 t/a municipal solid waste (MSW) into refuse-derived fuel (RDF) with high calorific value and recyclables.
9. What pricing options are available for accessing the report?
Pricing options include single-user, multi-user, and enterprise licenses priced at USD 3800, USD 4500, and USD 5800 respectively.
10. Is the market size provided in terms of value or volume?
The market size is provided in terms of value, measured in billion.
11. Are there any specific market keywords associated with the report?
Yes, the market keyword associated with the report is "China Waste to Energy Industry," which aids in identifying and referencing the specific market segment covered.
12. How do I determine which pricing option suits my needs best?
The pricing options vary based on user requirements and access needs. Individual users may opt for single-user licenses, while businesses requiring broader access may choose multi-user or enterprise licenses for cost-effective access to the report.
13. Are there any additional resources or data provided in the China Waste to Energy Industry report?
While the report offers comprehensive insights, it's advisable to review the specific contents or supplementary materials provided to ascertain if additional resources or data are available.
14. How can I stay updated on further developments or reports in the China Waste to Energy Industry?
To stay informed about further developments, trends, and reports in the China Waste to Energy Industry, consider subscribing to industry newsletters, following relevant companies and organizations, or regularly checking reputable industry news sources and publications.
Methodology
Step 1 - Identification of Relevant Samples Size from Population Database
Step 2 - Approaches for Defining Global Market Size (Value, Volume* & Price*)
Note*: In applicable scenarios
Step 3 - Data Sources
Primary Research
- Web Analytics
- Survey Reports
- Research Institute
- Latest Research Reports
- Opinion Leaders
Secondary Research
- Annual Reports
- White Paper
- Latest Press Release
- Industry Association
- Paid Database
- Investor Presentations
Step 4 - Data Triangulation
Involves using different sources of information in order to increase the validity of a study
These sources are likely to be stakeholders in a program - participants, other researchers, program staff, other community members, and so on.
Then we put all data in single framework & apply various statistical tools to find out the dynamic on the market.
During the analysis stage, feedback from the stakeholder groups would be compared to determine areas of agreement as well as areas of divergence


