Key Insights
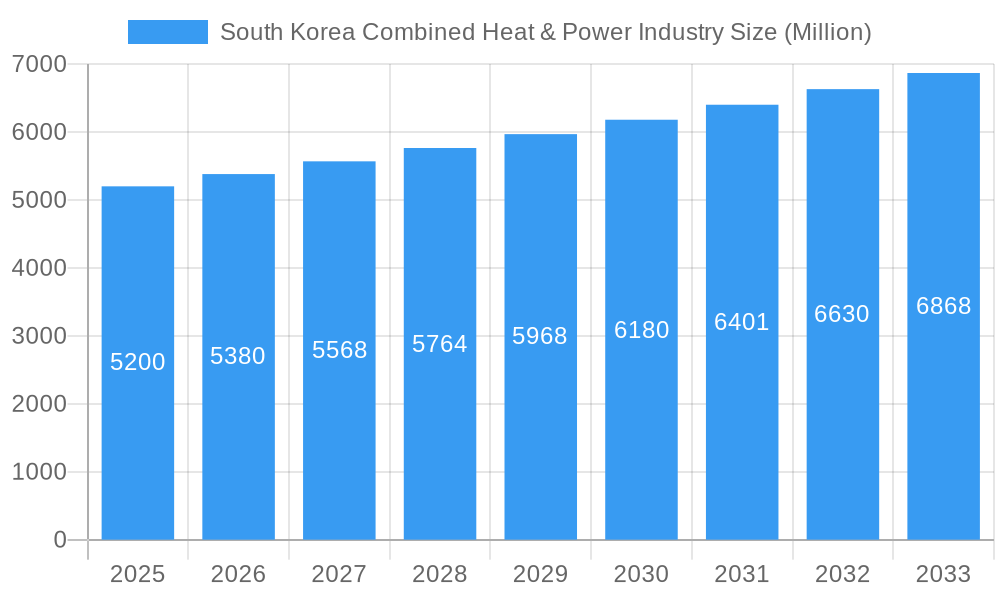
South Korea's Combined Heat and Power (CHP) market is projected for substantial growth, reaching an estimated $5.2 billion by 2025, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.6% through 2033. This expansion is driven by government initiatives focused on energy efficiency and decarbonization, alongside increasing energy needs in residential and commercial sectors. The adoption of cleaner fuels like natural gas supports South Korea's carbon reduction goals. Continuous demand from the industrial sector for stable, cost-effective energy solutions for manufacturing operations also fuels market growth. Technological advancements and smart grid development further enhance CHP plant efficiency and economic viability.
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Market Size (In Billion)
While promising, the South Korean CHP market faces challenges, notably high initial capital investment for plant installation, which can be a barrier for smaller businesses and developers. Stringent environmental regulations, although promoting cleaner fuels, also incur compliance costs for existing infrastructure. However, these restraints are being addressed through evolving government incentives, cost-reducing technological innovations, and increased awareness of CHP's long-term economic and environmental benefits. The market's diversification across residential, commercial & industrial (C&I), and utility sectors indicates broad demand, with C&I expected to lead due to high energy consumption. Key players, including Hanwha Engineering & Construction Corp, Siemens Energy AG, and Wärtsilä Oyj Abp, are actively shaping the market through innovation and strategic alliances.
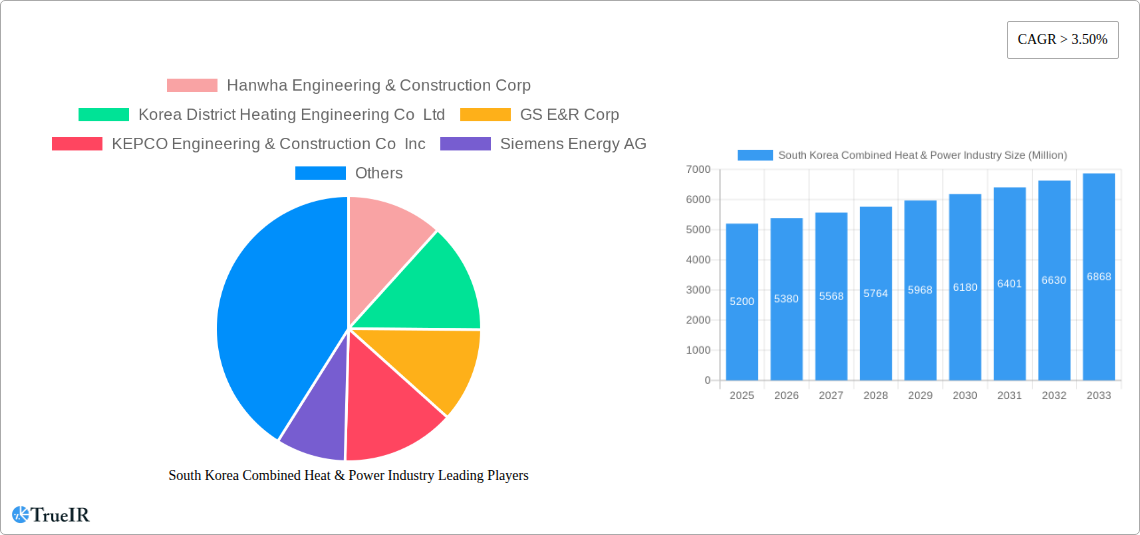
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Company Market Share
This comprehensive report analyzes the South Korea Combined Heat & Power (CHP) industry, detailing market size, growth drivers, competitive landscape, and future projections. Designed for industry professionals, investors, and policymakers, it provides in-depth insights into this dynamic sector using relevant SEO keywords. The study covers the period from 2019 to 2033, with 2024 as the base year and the market size estimated at $29.91 billion, with a forecast period from 2025–2033, including historical data from 2019–2024.
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Market Structure & Competitive Landscape
The South Korean Combined Heat & Power (CHP) market exhibits a moderately concentrated structure, with a blend of established domestic players and international technology providers. Innovation is primarily driven by the pursuit of enhanced energy efficiency, reduced emissions, and the integration of renewable energy sources within CHP systems. Regulatory frameworks, particularly those promoting energy saving and carbon reduction, play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. Product substitutes, such as standalone power generation and separate heating/cooling systems, are present but often lack the inherent efficiency advantages of CHP. End-user segmentation into Residential, Commercial and Industrial (C&I), and Utilities dictates varied demand drivers and technology adoption rates. Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity, while not consistently high, are indicative of consolidation opportunities and strategic partnerships aimed at expanding market reach and technological capabilities. Key M&A transactions are closely monitored for their potential to reshape competitive intensity and market share distribution. Concentration ratios are estimated to be around 60% for the top five players.
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Market Trends & Opportunities
The South Korean Combined Heat & Power (CHP) market is poised for significant growth, driven by escalating demand for energy efficiency, stringent environmental regulations, and the nation's strategic focus on decarbonization. Market size is projected to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 7.5% during the forecast period, reaching an estimated value of over 15 Billion by 2033. Technological shifts are leaning towards the adoption of more advanced and cleaner CHP solutions, including solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and advanced gas turbines, to improve overall system efficiency and minimize environmental impact. Consumer preferences are increasingly influenced by the desire for reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable energy solutions, making CHP an attractive proposition. Competitive dynamics are characterized by a healthy interplay between established players and emerging technology developers, fostering continuous innovation. Opportunities abound in the development of integrated energy solutions, smart grid compatibility, and the retrofitting of existing industrial facilities with CHP systems to capitalize on the growing emphasis on operational cost reduction and environmental responsibility. The penetration rate of CHP in the industrial sector is expected to rise substantially due to its inherent economic and ecological benefits, with a projected increase of over 15% by 2033.
Dominant Markets & Segments in South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry
The dominant market within South Korea's Combined Heat & Power (CHP) industry is clearly the Commercial and Industrial (C&I) segment. This dominance is underpinned by several key growth drivers, including the substantial energy demands of manufacturing facilities, large commercial complexes, and data centers, all of which benefit significantly from the cost savings and operational reliability offered by CHP systems. Robust government policies incentivizing industrial energy efficiency further bolster this segment.
- Commercial and Industrial (C&I) Segment: This segment is expected to represent over 60% of the total market revenue by 2033.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- High energy consumption in manufacturing, including semiconductors, automotive, and chemical industries.
- Increasing adoption by large commercial establishments like hotels, hospitals, and shopping malls for both power and heating/cooling needs.
- Government mandates and incentives for industrial energy efficiency and emission reduction.
- Technological advancements enabling the integration of CHP into complex industrial processes, thereby enhancing operational cost-effectiveness.
- Key Growth Drivers:
The Utilities segment also holds significant importance, particularly with the government's ongoing efforts to modernize the national power grid and diversify energy sources. The integration of CHP within utility infrastructure contributes to grid stability and provides a more resilient energy supply.
- Utilities Segment: This segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% during the forecast period.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Government initiatives for district heating networks and localized energy generation.
- The need for reliable baseload power generation to complement intermittent renewable sources.
- Investment in large-scale CHP plants for energy security and grid stability.
- Key Growth Drivers:
In terms of Fuel Type, Natural Gas is the overwhelmingly dominant fuel, accounting for an estimated 75% of the market share due to its availability, relatively lower emissions compared to coal, and established infrastructure.
- Natural Gas:
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Clean combustion characteristics and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Established supply chains and infrastructure.
- Government policies favoring cleaner fuel options.
- Technological advancements in natural gas-fired CHP engines and turbines.
- Key Growth Drivers:
While Coal and Oil were historically significant, their share is gradually declining due to environmental regulations and the push towards cleaner energy alternatives. Other Fuel Types, including biomass and waste-to-energy, are emerging as niche but growing segments, driven by sustainability initiatives and circular economy principles.
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Product Analysis
Product innovations in the South Korean CHP industry are focused on enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and improving integration capabilities. Advanced gas turbines and fuel cells, particularly solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), are gaining traction for their higher electrical efficiency and lower operational costs. Modular and scalable CHP systems are being developed to cater to a wider range of applications, from small commercial buildings to large industrial complexes. Competitive advantages lie in lower energy bills, a reduced carbon footprint, and enhanced energy security for end-users. The market is witnessing a growing demand for intelligent control systems that optimize energy generation and consumption in real-time, further boosting the appeal of modern CHP solutions.
Key Drivers, Barriers & Challenges in South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry
Key Drivers: The South Korean CHP market is propelled by stringent government policies promoting energy efficiency and carbon emission reductions, such as the National Energy Plan and R&D support for cleaner technologies. The increasing cost of electricity and growing awareness of environmental sustainability among businesses and consumers also act as significant drivers. Technological advancements in turbine efficiency and fuel cell technology are making CHP systems more economically viable and environmentally friendly, particularly in the Commercial and Industrial (C&I) sector where operational cost savings are substantial.
Barriers & Challenges: High initial capital investment remains a primary barrier to widespread adoption, especially for smaller enterprises. Complex regulatory approval processes and grid connection challenges can also hinder project development. Furthermore, the fluctuating prices of natural gas, the dominant fuel, introduce economic uncertainties. Supply chain disruptions for specialized components and the availability of skilled labor for installation and maintenance pose ongoing challenges. Competitive pressure from standalone renewable energy sources and traditional power generation methods also needs to be addressed. For instance, the cost of installing a typical 10 MW industrial CHP system can range from 15 Million to 25 Million, representing a significant upfront expenditure.
Growth Drivers in the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Market
The growth of the South Korean Combined Heat & Power (CHP) market is primarily fueled by government mandates and incentives aimed at achieving national energy efficiency targets and reducing carbon emissions. Significant investments in research and development for cleaner and more efficient CHP technologies, such as advanced fuel cells and waste-to-energy systems, are creating new opportunities. The increasing demand from the Commercial and Industrial (C&I) sector, driven by the need to lower operational costs and enhance energy resilience, is another major growth catalyst. Furthermore, the expansion of district heating networks and the focus on localized energy generation contribute to market expansion.
Challenges Impacting South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Growth
Despite robust growth prospects, the South Korean CHP industry faces several challenges. High upfront capital investment for CHP installations remains a significant hurdle, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. Regulatory complexities and lengthy approval processes can delay project implementation. The volatile pricing of natural gas, the predominant fuel, introduces economic uncertainty and impacts the return on investment. Moreover, the availability of skilled labor for the installation, operation, and maintenance of advanced CHP systems is a growing concern, potentially leading to project delays and increased operational costs.
Key Players Shaping the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Market
- Hanwha Engineering & Construction Corp
- Korea District Heating Engineering Co Ltd
- GS E&R Corp
- KEPCO Engineering & Construction Co Inc
- Siemens Energy AG
- General Electric Company
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd
- Wärtsilä Oyj Abp
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
Significant South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Industry Milestones
- July 2021: Bloom Energy, a United States-based green energy company, announced its first combined heat and power (CHP) project in collaboration with SK Ecoplant (formerly known as SK Engineering and Construction). The new 4.2-megawatt (MW) installation marked South Korea's first-ever utility-scale solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) CHP initiative, signifying a major advancement in fuel cell technology adoption for CHP in the country.
Future Outlook for South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Market
The future outlook for the South Korean Combined Heat & Power (CHP) market is exceptionally bright, characterized by sustained growth driven by a confluence of supportive government policies, technological advancements, and increasing environmental consciousness. The ongoing transition towards cleaner energy sources and the imperative to enhance energy efficiency will continue to propel demand for CHP solutions, particularly within the Commercial and Industrial (C&I) sector. Strategic opportunities lie in the development of highly efficient and low-emission CHP systems, the integration of smart grid technologies, and the expansion of applications into emerging sectors like data centers and smart cities. Investments in hydrogen fuel cell CHP technologies are also expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the long-term growth trajectory of the market.
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Segmentation
-
1. Application
- 1.1. Residential
- 1.2. Commercial and Industrial (C&I)
- 1.3. Utilities
-
2. Fuel Type
- 2.1. Natural Gas
- 2.2. Coal
- 2.3. Oil
- 2.4. Other Fuel Types
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Segmentation By Geography
- 1. South Korea
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Regional Market Share
Geographic Coverage of South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry
South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry REPORT HIGHLIGHTS
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2020-2034 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Estimated Year | 2026 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 5.6% from 2020-2034 |
| Segmentation |
|
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 1.1. Research Scope
- 1.2. Market Segmentation
- 1.3. Research Methodology
- 1.4. Definitions and Assumptions
- 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Introduction
- 3. Market Dynamics
- 3.1. Introduction
- 3.2. Market Drivers
- 3.2.1. 4.; Increasing Population Growth and Infrastructure Development
- 3.3. Market Restrains
- 3.3.1. 4.; High Operational and Maintenance Costs
- 3.4. Market Trends
- 3.4.1. Natural Gas Segment to Witness Significant Demand
- 4. Market Factor Analysis
- 4.1. Porters Five Forces
- 4.2. Supply/Value Chain
- 4.3. PESTEL analysis
- 4.4. Market Entropy
- 4.5. Patent/Trademark Analysis
- 5. South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Analysis, Insights and Forecast, 2020-2032
- 5.1. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Application
- 5.1.1. Residential
- 5.1.2. Commercial and Industrial (C&I)
- 5.1.3. Utilities
- 5.2. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Fuel Type
- 5.2.1. Natural Gas
- 5.2.2. Coal
- 5.2.3. Oil
- 5.2.4. Other Fuel Types
- 5.3. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Region
- 5.3.1. South Korea
- 5.1. Market Analysis, Insights and Forecast - by Application
- 6. Competitive Analysis
- 6.1. Market Share Analysis 2025
- 6.2. Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Hanwha Engineering & Construction Corp
- 6.2.1.1. Overview
- 6.2.1.2. Products
- 6.2.1.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.1.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.1.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.2 Korea District Heating Engineering Co Ltd
- 6.2.2.1. Overview
- 6.2.2.2. Products
- 6.2.2.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.2.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.2.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.3 GS E&R Corp
- 6.2.3.1. Overview
- 6.2.3.2. Products
- 6.2.3.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.3.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.3.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.4 KEPCO Engineering & Construction Co Inc
- 6.2.4.1. Overview
- 6.2.4.2. Products
- 6.2.4.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.4.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.4.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.5 Siemens Energy AG
- 6.2.5.1. Overview
- 6.2.5.2. Products
- 6.2.5.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.5.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.5.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.6 General Electric Company
- 6.2.6.1. Overview
- 6.2.6.2. Products
- 6.2.6.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.6.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.6.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.7 Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd
- 6.2.7.1. Overview
- 6.2.7.2. Products
- 6.2.7.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.7.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.7.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.8 Wärtsilä Oyj Abp
- 6.2.8.1. Overview
- 6.2.8.2. Products
- 6.2.8.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.8.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.8.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.9 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- 6.2.9.1. Overview
- 6.2.9.2. Products
- 6.2.9.3. SWOT Analysis
- 6.2.9.4. Recent Developments
- 6.2.9.5. Financials (Based on Availability)
- 6.2.1 Hanwha Engineering & Construction Corp
List of Figures
- Figure 1: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Revenue Breakdown (billion, %) by Product 2025 & 2033
- Figure 2: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Share (%) by Company 2025
List of Tables
- Table 1: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Application 2020 & 2033
- Table 2: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Volume Gigawatt Forecast, by Application 2020 & 2033
- Table 3: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Fuel Type 2020 & 2033
- Table 4: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Volume Gigawatt Forecast, by Fuel Type 2020 & 2033
- Table 5: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Region 2020 & 2033
- Table 6: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Volume Gigawatt Forecast, by Region 2020 & 2033
- Table 7: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Application 2020 & 2033
- Table 8: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Volume Gigawatt Forecast, by Application 2020 & 2033
- Table 9: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Fuel Type 2020 & 2033
- Table 10: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Volume Gigawatt Forecast, by Fuel Type 2020 & 2033
- Table 11: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Revenue billion Forecast, by Country 2020 & 2033
- Table 12: South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry Volume Gigawatt Forecast, by Country 2020 & 2033
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry?
The projected CAGR is approximately 5.6%.
2. Which companies are prominent players in the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry?
Key companies in the market include Hanwha Engineering & Construction Corp, Korea District Heating Engineering Co Ltd, GS E&R Corp, KEPCO Engineering & Construction Co Inc, Siemens Energy AG, General Electric Company, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd, Wärtsilä Oyj Abp, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
3. What are the main segments of the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry?
The market segments include Application, Fuel Type.
4. Can you provide details about the market size?
The market size is estimated to be USD 29.91 billion as of 2022.
5. What are some drivers contributing to market growth?
4.; Increasing Population Growth and Infrastructure Development.
6. What are the notable trends driving market growth?
Natural Gas Segment to Witness Significant Demand.
7. Are there any restraints impacting market growth?
4.; High Operational and Maintenance Costs.
8. Can you provide examples of recent developments in the market?
In July 2021, Bloom Energy, the United States-based green energy company, announced its first combined heat and power (CHP) project in collaboration with SK Ecoplant (formerly known as SK Engineering and Construction). The new 4.2-megawatt (MW) installation marks South Korea's first-ever utility-scale solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) CHP initiative.
9. What pricing options are available for accessing the report?
Pricing options include single-user, multi-user, and enterprise licenses priced at USD 3800, USD 4500, and USD 5800 respectively.
10. Is the market size provided in terms of value or volume?
The market size is provided in terms of value, measured in billion and volume, measured in Gigawatt.
11. Are there any specific market keywords associated with the report?
Yes, the market keyword associated with the report is "South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry," which aids in identifying and referencing the specific market segment covered.
12. How do I determine which pricing option suits my needs best?
The pricing options vary based on user requirements and access needs. Individual users may opt for single-user licenses, while businesses requiring broader access may choose multi-user or enterprise licenses for cost-effective access to the report.
13. Are there any additional resources or data provided in the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry report?
While the report offers comprehensive insights, it's advisable to review the specific contents or supplementary materials provided to ascertain if additional resources or data are available.
14. How can I stay updated on further developments or reports in the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry?
To stay informed about further developments, trends, and reports in the South Korea Combined Heat & Power Industry, consider subscribing to industry newsletters, following relevant companies and organizations, or regularly checking reputable industry news sources and publications.
Methodology
Step 1 - Identification of Relevant Samples Size from Population Database
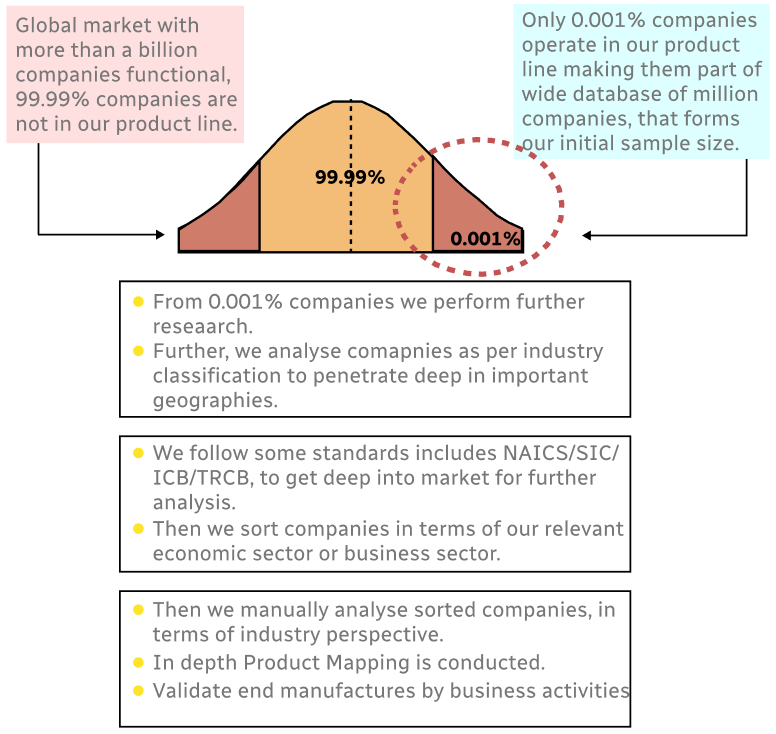
Step 2 - Approaches for Defining Global Market Size (Value, Volume* & Price*)
Note*: In applicable scenarios
Step 3 - Data Sources
Primary Research
- Web Analytics
- Survey Reports
- Research Institute
- Latest Research Reports
- Opinion Leaders
Secondary Research
- Annual Reports
- White Paper
- Latest Press Release
- Industry Association
- Paid Database
- Investor Presentations
Step 4 - Data Triangulation
Involves using different sources of information in order to increase the validity of a study
These sources are likely to be stakeholders in a program - participants, other researchers, program staff, other community members, and so on.
Then we put all data in single framework & apply various statistical tools to find out the dynamic on the market.
During the analysis stage, feedback from the stakeholder groups would be compared to determine areas of agreement as well as areas of divergence


